Arthritis occurs due to the calcium pyrophosphate is known to confuse doctors most often. This condition is often confused with gout or other conditions. Hence, to identify the condition, a proper diagnosis is required. If this condition is ignored or the treatment is delayed, chronic inflammation and pain may be noticed. Besides this, the affected person will also experience long-term disability of the affected joint. Severe cases may require surgical intervention using Orthopaedic Implants to repair or replace the damaged joint.
This form of arthritis is known as calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease, and we will talk about it in this post.
What is Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition Disease (CPPD)?
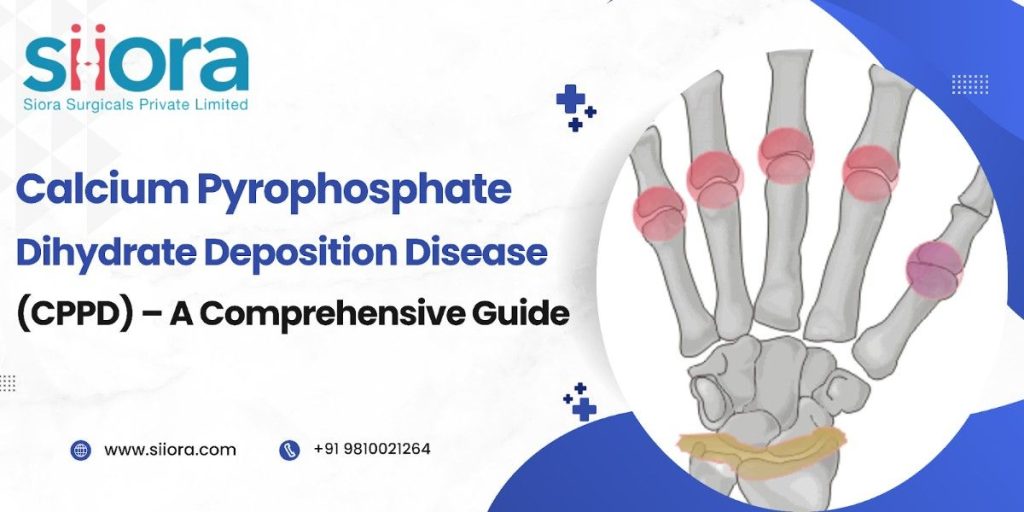
Also known as pseudogout, CPPD is a type of arthritis that is known to show gout-like symptoms. In most cases, the condition affects only one joint but, sometimes it can also affect more than one joint. In certain cases, the symptoms shown by the condition may resemble that of rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis. Some of the common locations where CPPD is experienced include:
- Knees
- Wrists
- Ankles
- Shoulders
- Hands
- Elbows
Knees and wrists are the most commonly affected sites by calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease.
Who is More Affected by CPPD?
CPPD is known to affect people above 60 years of age more, and both men and women are equally affected. Besides this, there are certain risk factors associated with the condition, and they include:
- Health condition related to thyroid
- Kidney failure
- The low magnesium content in the body
- Hemochromatosis and other conditions that affect iron, calcium, or phosphate metabolism
- Parathyroid disease
Besides all this, people who are suffering from degenerative joint disease or osteoarthritis are also at high risk of developing CPPD.
What Are the Symptoms Associated with CPPD?
The symptoms seen in the case of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease may include:
- Severe pain and swelling in one or more joints
- Warm and tender to touch joints
- Redness on the affected joint
Sometimes, CPPD may mimic the symptoms seen in rheumatoid arthritis, but such a situation is not common.
What Are the Causes of CPPD?
When the abnormal formation of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals in the cartilages or joint fluid occurs, sudden attacks of arthritis may be experienced that mimic gout. Now, the point to be noticed here is that the reason why CPPD crystals deposit in the cartilage is unknown. Besides this, the condition may also occur as a result of an injury to the joint, hemochromatosis, hypothyroidism, and hyperparathyroidism. In some cases, it may also be a hereditary condition.
How is CPPD Diagnosed?
Synovial fluid from the inflamed joint is aspirated for microscopic examination to find out whether pyrophosphate crystals have been deposited or not. Arthrocentesis is the process of aspirating synovial fluid from the joint. Besides this, imaging tests like X-ray or CT scans may also be performed to ensure the highest accuracy of the diagnosis of the condition. But still, the synovial fluid examination is known to deliver the best results.
How CPPD is Treated?
Anti-inflammatory medication is often prescribed to relieve the symptoms of CPPD, and it is noticed that effects are seen within 24 hours after the start of the treatment. The treatment aims to relieve symptoms like pain and inflammation plus, reduce the risk of sudden gout-like attacks that may result in joint damage.
In the most severe cases, surgery to repair or replace the damaged joint may be done.
Siora Surgicals Pvt. Ltd. is an experienced orthopedic manufacturer in India that produces all types of trauma implants conforming to ISO 13485:2016 standards. The company is also looking to establish its presence as one of the best Orthopaedic Device Companies in Ukraine.